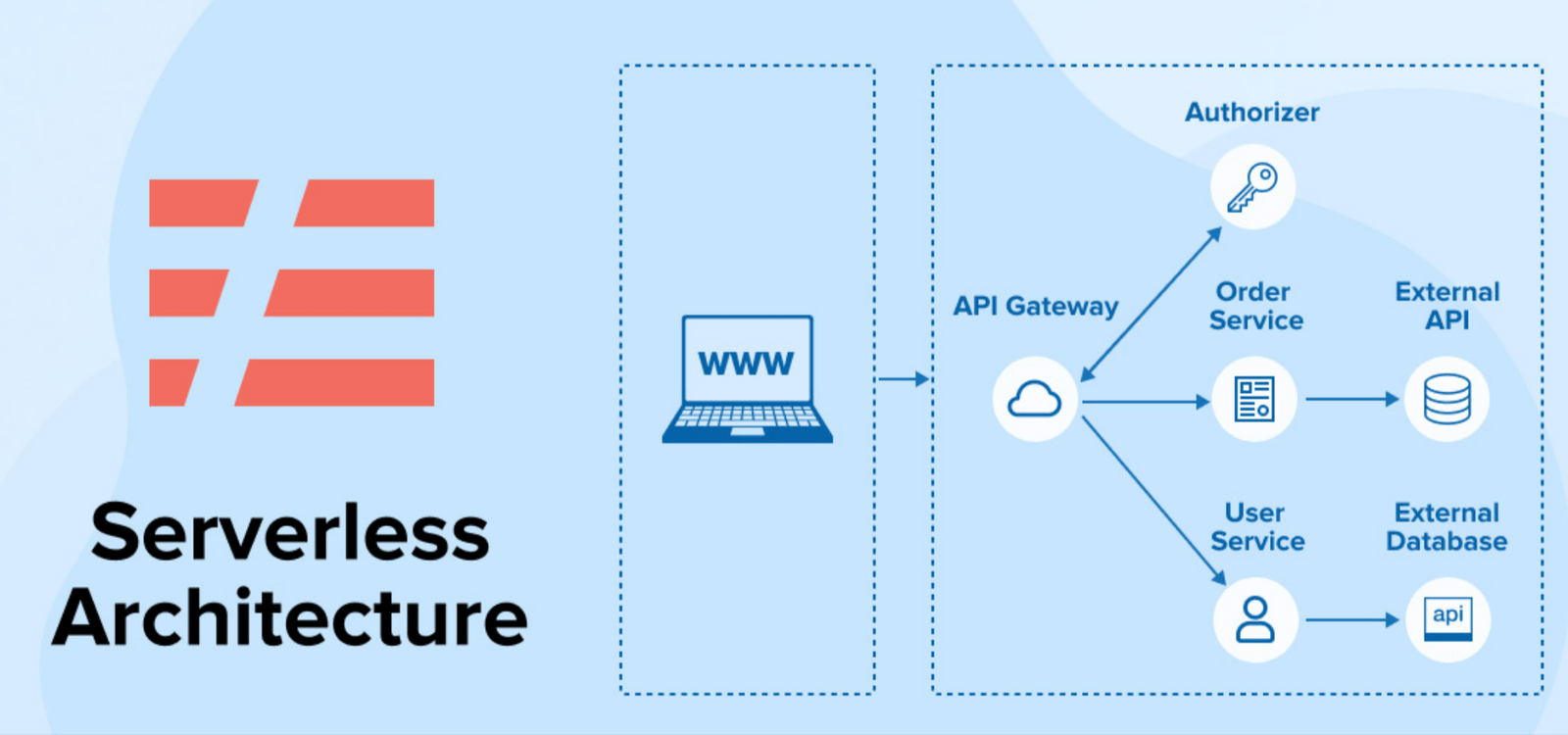
In recent years, serverless architectures have gained significant traction within the software development community. This paradigm shift is characterized by the abstraction of server management, allowing developers to focus on writing code without the burden of provisioning or maintaining servers. The term “serverless” can be somewhat misleading, as servers are still involved in the execution of applications; however, the management of these servers is entirely handled by cloud service providers.
This model has emerged as a response to the increasing demand for agility and efficiency in application development, driven by the rapid pace of technological advancement and the need for businesses to innovate quickly. The rise of serverless architectures can be attributed to several factors, including the proliferation of cloud computing and the growing complexity of applications. As organizations seek to leverage cloud capabilities, they are increasingly turning to serverless solutions to streamline their development processes.
The ability to deploy applications in a more modular fashion allows teams to iterate quickly and respond to changing market demands. Furthermore, serverless architectures facilitate a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can lead to significant cost savings for businesses that experience fluctuating workloads. This combination of flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness has made serverless architectures an attractive option for organizations of all sizes.
The Shift from Monolithic to Microservices
The transition from monolithic architectures to microservices has been a defining trend in software development over the past decade. Monolithic applications are built as a single, unified unit, which can lead to challenges in scalability, maintainability, and deployment. In contrast, microservices architecture breaks down applications into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
This shift has been instrumental in enabling organizations to adopt more agile development practices and respond more effectively to user needs. Serverless architectures complement the microservices approach by providing a framework that allows developers to deploy individual functions or services without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Each microservice can be executed in response to specific events, such as HTTP requests or database changes, making it easier to build responsive and scalable applications.
This decoupling of services not only enhances flexibility but also fosters a culture of continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), where teams can release updates more frequently and with greater confidence. As organizations embrace this shift, they are discovering that serverless architectures can significantly reduce the time and effort required to bring new features to market.
The Advantages of Serverless Application Deployment

One of the most compelling advantages of serverless application deployment is its inherent scalability. In traditional architectures, scaling an application often requires significant planning and resource allocation, which can be both time-consuming and costly. With serverless architectures, however, scaling is handled automatically by the cloud provider.
When demand for an application spikes, additional resources are provisioned seamlessly in real-time, ensuring that performance remains consistent without manual intervention. This elasticity allows businesses to accommodate varying workloads without over-provisioning resources during periods of low demand. Another key benefit of serverless deployment is the reduction in operational overhead.
Developers can focus on writing code and delivering features rather than managing infrastructure. This shift not only accelerates development cycles but also reduces the likelihood of human error associated with server management tasks. Additionally, serverless architectures often come with built-in monitoring and logging capabilities, providing developers with valuable insights into application performance and user behavior.
This data-driven approach enables teams to make informed decisions about optimizations and improvements, ultimately leading to better user experiences.
The Role of Cloud Providers in Serverless Architectures
| Cloud Provider | Serverless Offerings | Compute Services | Storage Services | Networking Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Lambda, API Gateway, DynamoDB, S3 | AWS Lambda, AWS Fargate, AWS EC2 | Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, Amazon Glacier | Amazon VPC, Amazon Route 53, AWS Direct Connect |
| Microsoft Azure | Azure Functions, Azure Logic Apps, Cosmos DB, Blob Storage | Azure Functions, Azure Virtual Machines, Azure Kubernetes Service | Azure Blob Storage, Azure Files, Azure Data Lake Storage | Azure Virtual Network, Azure Load Balancer, Azure Traffic Manager |
| Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Cloud Functions, Cloud Run, Firestore, Cloud Storage | Google Cloud Functions, Google Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine | Google Cloud Storage, Google Cloud Bigtable, Google Cloud Filestore | Google Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Cloud Load Balancing, Cloud CDN |
Cloud providers play a pivotal role in the success of serverless architectures by offering the necessary infrastructure and services that enable developers to build and deploy applications without managing servers directly. Major players in this space include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), each providing their own serverless offerings such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions. These platforms abstract away the complexities of server management while providing robust tools for building scalable applications.
The competitive landscape among cloud providers has led to rapid innovation in serverless technologies. Providers continuously enhance their offerings with new features, integrations, and performance improvements. For instance, AWS Lambda allows developers to run code in response to events from various AWS services, while Azure Functions supports a wide range of programming languages and integrates seamlessly with other Azure services.
This level of integration not only simplifies the development process but also enables organizations to leverage existing cloud resources effectively. As cloud providers continue to evolve their serverless offerings, they are shaping the future of application development and deployment.
The Impact of Serverless Architectures on DevOps
The adoption of serverless architectures has had a profound impact on DevOps practices within organizations. By enabling teams to deploy applications more rapidly and efficiently, serverless technologies align closely with the core principles of DevOps: collaboration, automation, and continuous delivery. The ability to deploy individual functions or microservices independently allows teams to adopt a more iterative approach to development, where features can be released incrementally rather than waiting for a large monolithic deployment.
Moreover, serverless architectures facilitate automation through event-driven workflows. Developers can set up triggers that automatically invoke functions based on specific events, such as changes in data or user interactions. This level of automation not only streamlines deployment processes but also enhances overall system reliability by reducing the potential for human error during deployments.
As organizations embrace DevOps practices alongside serverless architectures, they are finding that they can achieve faster time-to-market while maintaining high levels of quality and performance.
The Evolution of Application Scalability with Serverless Architectures

Scalability has always been a critical consideration in application design, but traditional approaches often required careful planning and resource allocation. With the advent of serverless architectures, scalability has evolved into a more dynamic and automated process. In a serverless environment, applications can scale up or down based on real-time demand without manual intervention from developers or operations teams.
This capability is particularly beneficial for applications with unpredictable traffic patterns or seasonal spikes in usage. For example, consider an e-commerce platform that experiences significant traffic during holiday sales events. In a traditional architecture, the organization would need to provision additional servers ahead of time to handle the increased load, which could lead to wasted resources during off-peak times.
In contrast, a serverless architecture would automatically allocate resources as needed during peak traffic periods and scale back down when demand subsides. This not only optimizes resource utilization but also ensures that users have a seamless experience regardless of fluctuations in traffic.
The Challenges of Serverless Application Deployment
Despite its many advantages, serverless application deployment is not without its challenges. One significant concern is vendor lock-in; organizations may find themselves heavily reliant on a specific cloud provider’s services and tools. This dependency can make it difficult to migrate applications or switch providers if business needs change or if a more cost-effective solution becomes available.
To mitigate this risk, organizations must carefully evaluate their options and consider adopting multi-cloud strategies that allow them to leverage multiple providers while minimizing reliance on any single vendor. Another challenge associated with serverless architectures is the complexity of debugging and monitoring applications. In a traditional environment, developers have direct access to servers and can easily troubleshoot issues as they arise.
However, in a serverless context, where functions may be executed across distributed environments, identifying the root cause of problems can be more difficult. Developers must rely on logging and monitoring tools provided by cloud providers or third-party solutions to gain visibility into application performance. Ensuring that these tools are properly configured and integrated into the development workflow is essential for maintaining application reliability.
The Future of Application Deployment with Serverless Architectures
As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation initiatives, the future of application deployment is likely to be heavily influenced by serverless architectures. The ongoing evolution of cloud technologies will drive further advancements in serverless capabilities, making it easier for developers to build complex applications without being bogged down by infrastructure concerns. Innovations such as improved tooling for monitoring and debugging will enhance developers’ ability to manage serverless applications effectively.
Moreover, as businesses increasingly prioritize agility and responsiveness in their operations, serverless architectures will become an integral part of their technology stacks. The ability to deploy applications quickly while minimizing operational overhead will be crucial for organizations looking to stay competitive in fast-paced markets. As more companies adopt serverless solutions, we can expect to see an expansion in use cases across various industries—from e-commerce and finance to healthcare and entertainment—demonstrating the versatility and potential of this architectural paradigm.
In conclusion, the rise of serverless architectures represents a significant shift in how applications are developed and deployed. By enabling organizations to focus on code rather than infrastructure management, serverless solutions are transforming the landscape of software development and paving the way for more agile and efficient practices in the future.
FAQs
What is a serverless architecture?
A serverless architecture is a cloud computing model where the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation and provisioning of servers. This means that developers do not have to worry about server management, and can focus solely on writing and deploying code.
How does serverless architecture change application deployment?
Serverless architecture changes application deployment by allowing developers to deploy code without having to manage servers. This means that developers can focus on writing and deploying code, without having to worry about server provisioning, scaling, or maintenance.
What are the benefits of serverless architectures for application deployment?
Some benefits of serverless architectures for application deployment include reduced operational overhead, automatic scaling, and pay-per-use pricing. Additionally, serverless architectures can lead to faster development cycles and increased agility for development teams.
What are some popular serverless platforms for application deployment?
Some popular serverless platforms for application deployment include AWS Lambda, Microsoft Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions, and IBM Cloud Functions. These platforms provide the infrastructure and tools necessary for developers to deploy serverless applications.
What are some challenges of using serverless architectures for application deployment?
Some challenges of using serverless architectures for application deployment include vendor lock-in, limited control over the underlying infrastructure, and potential performance issues with cold starts. Additionally, serverless architectures may not be suitable for all types of applications, such as those with long-running processes or specific networking requirements.